Computer Science 105 Assignment 6 - Computer Organization and
Programming
Due: 5:00pm October 24, 2003
Objectives and Overview: This assignment introduces some basic
ideas about computer organization with programming and algorithm
design. The key question addressed here is, "How does a
computer carry out the steps
of an algorithm?" The readings and exercises for this assignment are
taken
from portions of chapters 5 and 6 of your text.
Part 1 - Translate a Program to Machine Language
Following the same steps that you used for Assignment 2, locate the icon
Invitation (OSX) that appears in the folder Invitation on
your
desktop, and activate the familiar orange menu. The button
Assembler
is used for this assignment. When you select it, Open the
file
EXAMPLE1.ASM in the Invitation -> Examples directory, and
then
select Assemble in the Assembler menu. The following
result
should appear on your screen.
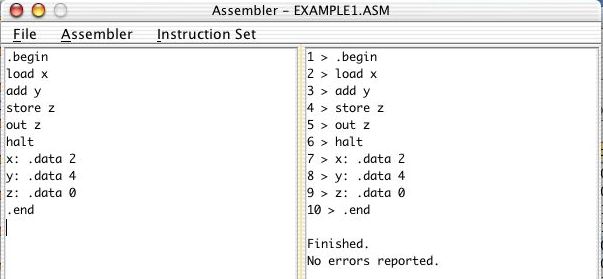
This window has two columns. On the left is a listing of the
original assembly language program and on the right is a copy of that
listing that is checked for errors and has been translated into machine
code. The actual machine code doesn't appear until you select Execute
in the Assembler menu. At that point, the following additional
window will open.
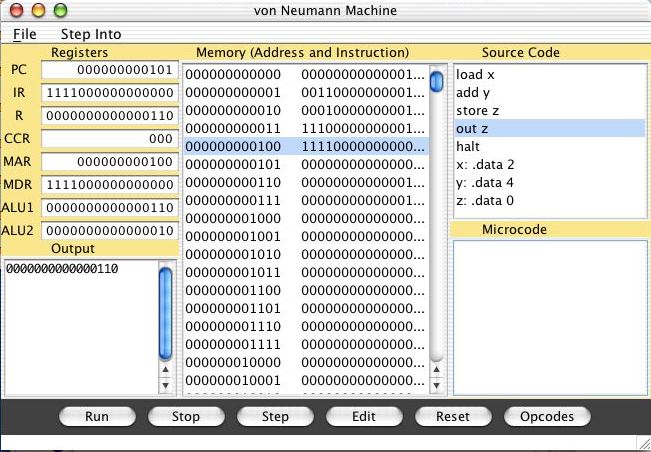
This is a simulator for the machine that is introduced and discussed
in Chapter 5. In the right-hand window is the original Assembly
language program and in the center is the (binary) representation of
the machine instructions that correspond to each instruction in that
program. You should refer to Chapter 5 for more details about the
role of the PC, IR, etc in the left-hand column and the structure of
the machine instructions themselves.
To run this program, select the Run button and observe that
a binary number appears in the Output window on the left. You
should get the same result that appears above.
1. Describe in pseudocode what this program does.
At the machine level, everything is done in binary, including input
and output. Running some programs, such as EXAMPLE2.ASM, requires
binary input, which is prompted by the following "Cell Editor" window
where you can
enter the 0s and 1s that make up a binary number:
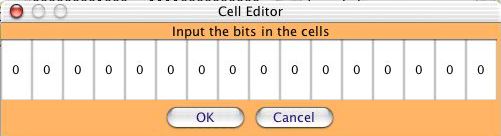
Run the program EXAMPLE2.ASM by entering the binary input requested
and observing the Output window's contents when the program halts.
2. Describe in pseudocode or in English what this program does.
Now run the program EXAMPLE3.ASM in the same fashion.
3. Describe in pseudocode or in English what this program does.
Part 3 - Algorithmic Problem Solving
Complete your answers to the above three questions, and then complete
Exercise 18 on page 229 and Exercises 5, 7, 10, 11, and 12 on page 285
of your text. You should complete exercise 12 by modifying the
Assembly language program EXAMPLE3.ASM (this is equivalent to the
program in Figure 6.8 of your text) and using the software tools
described above, and submit your program to the csci105 -> Drop
Box.
You may do these exercises (except the last one) either by hand or with
a word processor. Also, you may choose to do this assignment either by
yourself or in teams of two. If you work with someone else, the
team may hand in one copy of the completed exercises with both names at
the top.
Part 4 - Submitting Your Work
To submit a file electronically, remember to rename it so that you are
identified as the author (e.g., give it a name like asst6atucker).
Then drag the file to the csci105 -> Drop Box folder.
To submit a handwritten assignment, leave it in the CS105
mailbox near my office (Searles 220).
